

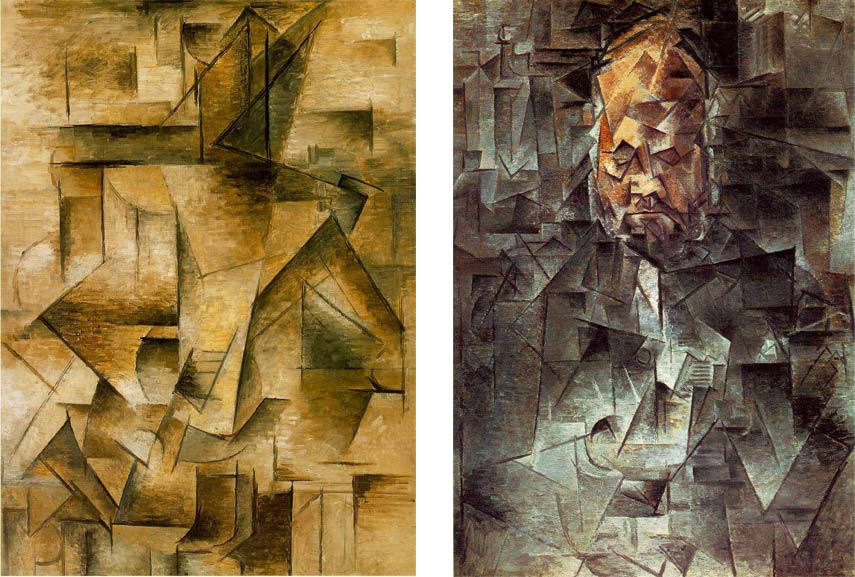
It may not be possible, for two simple reasons.
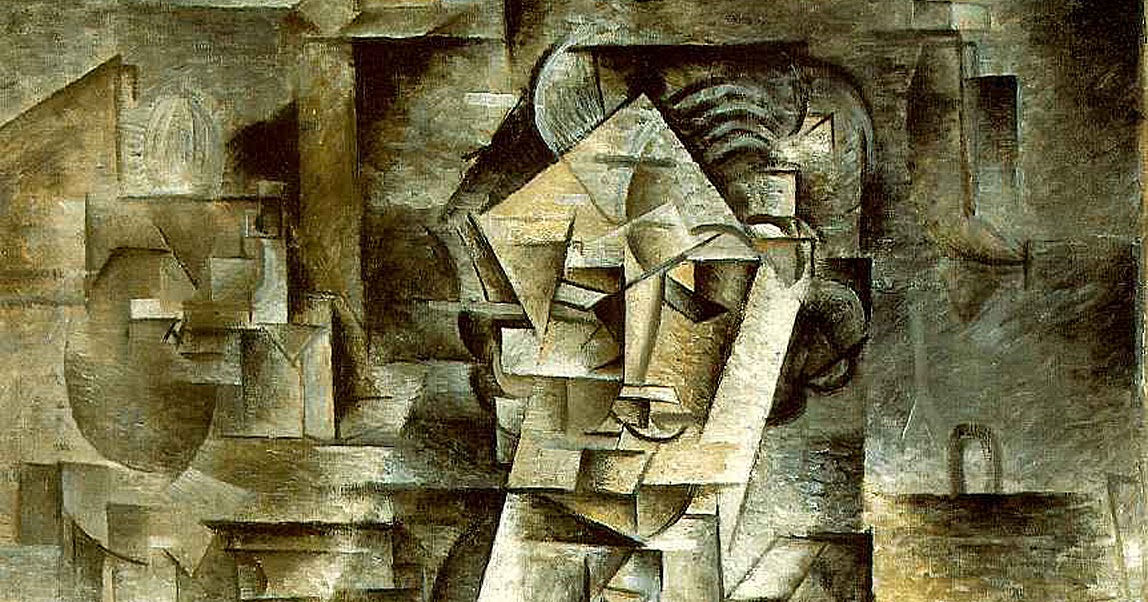

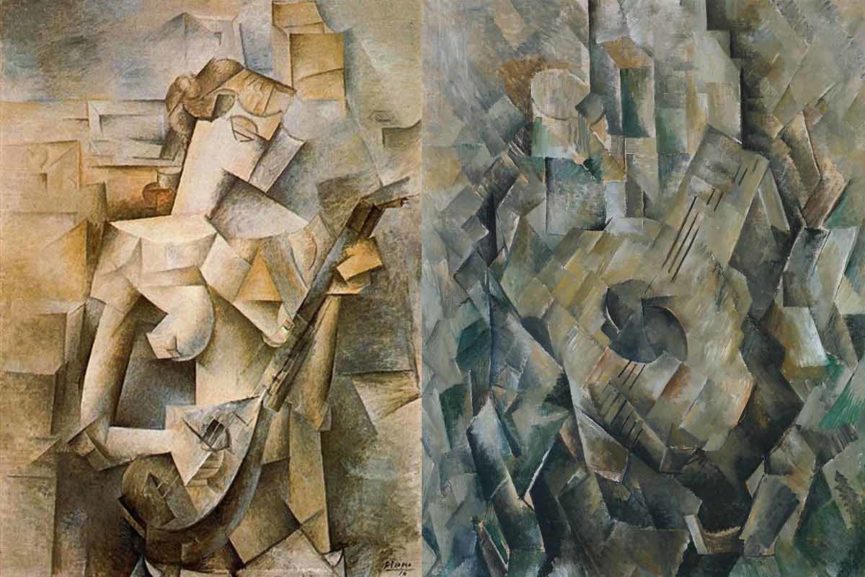
If critics want to demonstrate Cubism’s values, they only need to take a picture like Ma Jolie (1912) and show how the pretty girl in the title can be reconstructed. Many of the devices were intended to flatten the image plane and reduce depth. Synthetic Cubism was thought to force objects together rather than divide them to analyze them. Cubist paintings are paintings based on newspaper clippings, sheet music, cloth, and painted text. During the 1920s and 1930s, Picasso was the first to use collage and collage in his fine art paintings. Analytical Cubism and Synthetic Cubism are two major branches of Cubism. Cubism emerged from a desire to break with the past and change the meaning of art. Cubism was divided into three stages: first, the Cezanian Cubism then, the Analytical Cubism and finally, the Synthetic Cubism.Ī sudden change in style occurs in Picasso’s Les Demoiselles d’Avignon, which depicts African and primitive forms of art. What Are The 3 Types Of Cubism?Ĭubism can be classified into three types. Blocks would be viewed from a variety of angles. Artists would study (or analyze) the subject and divide it into multiple sections in this style. It was believed that the letters were flat shapes that could not be distorted because they existed outside the universe, so being close to space, the letters represented objects far away whereas having a presence in the painting enabled one to distinguish between objects standing in space and those in outer space.Īnalytical Cubism is the movement’s first stage. In fact, the Renaissance concept of a painting being a window into a receding world is still prevalent. In general, colors such as tan, brown, gray, cream, green, or blue were thought to be nearly monochromatic (hues of tan, brown, gray, cream, green, or blue are preferred). The outlines of even objects began to fade during the analytical phase, making them even less identifiable as a result. Another aspect of unconventional coloration was to distort an object’s appearance. In this time period, about 1908 to 1911, the quality of fragmentation, or cubist quality, deteriorated because planes were overlapping. An analytical cubism is a type of cubism that is considered to be the first. This style was influenced by the Cubist artists’ newfound interest in the properties of light and reflection.Įxamples of Cubism’s three stages can be found here. In this phase, the artists further simplified their compositions, creating works that were composed of highly faceted geometric forms. The third and final phase of Cubism, known as Crystal Cubism, lasted from 1914 to 1918. This was done by incorporating collage elements such as newspaper clippings and bits of fabric into their paintings. In this phase, the artists began to synthesize their deconstructed forms into new, more abstract compositions. The second phase of Cubism, known as Synthetic Cubism, lasted from 1912 to 1914. This was done in order to achieve a greater understanding of the underlying structure of the objects. In this phase, Picasso and Braque deconstructed the natural forms of their subjects, reducing them to their basic geometric shapes. The first phase of Cubism, known as Analytical Cubism, lasted from 1908 to 1912. This revolutionary style had a profound impact on the development of modern art, and its influence can still be seen in contemporary art movements. Led by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, Cubism was characterized by its geometric forms and fragmented, multitonal surfaces. there is very little tonal differentiation used: the general tone of works tends to be muted with a similar dark tone used across the paintings.In the early 20th century, an avant-garde art movement known as Cubism arose in France.they are painted using a limited range of dark colours (mainly blacks, greys and ochres).they appear as a busy interweaving of planes and lines with the subjects fractured, or broken up.The main characteristics of analytical cubist paintings are: Braque tended to show objects exploding out into fragments, while Picasso rendered them magnetized, with attracting forces compelling elements of the pictorial space into the center of the composition. Although Picasso and Braque's works were often similar in appearance, their separate interests showed through over time. In this phase the artists restricted their subject matter to the traditional genres of portraiture and still life and also limited their colours to earth tones and muted greys. The name ‘analytic’ coined by Juan Gris suggests that the technique involved a close examination and analysis of objects in order to translate it into geometric shapes, angles and lines. The Analytic Cubism developed between 19.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
